Difference between revisions of "Extrasystole"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
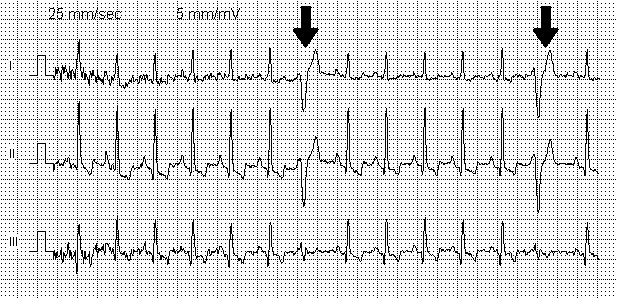
[[File:Extrasystole.png|right]]<b>Extrasystole (premature contractions)</b> is untimely depolarization and contraction of the heart or its individual chambers, it is the most frequently recorded form of [[Arrhythmia and its types|arrhythmias]]. Extrasystoles can be found in 60-70% of people. Basically they are functional (neurogenic), their appearance is provoked by stress, smoking, alcohol, strong tea and especially coffee. Extrasystoles of organic origin arise from damage to the myocardium (ischaemic heart disease, cardiosclerosis, dystrophy, inflammation). [1] | [[File:Extrasystole.png|right]]<b>Extrasystole (premature contractions)</b> is untimely depolarization and contraction of the heart or its individual chambers, it is the most frequently recorded form of [[Arrhythmia and its types|arrhythmias]]. Extrasystoles can be found in 60-70% of people. Basically they are functional (neurogenic), their appearance is provoked by stress, smoking, alcohol, strong tea and especially coffee. Extrasystoles of organic origin arise from damage to the myocardium (ischaemic heart disease, cardiosclerosis, dystrophy, inflammation). [1] | ||
It is manifested by the sensation of a strong heartbeat, a sensations of interruptions in the work of the heart, anxiety, lack of air. Reduction of cardiac output in extrasystole leads to a decrease in coronary and cerebral blood flow and can lead to the development of angina pectoris and transient disorders of cerebral circulation (fainting, paresis, etc.). Extrasystoles increase the risk of [[atrial fibrillation]] and sudden death. | It is manifested by the sensation of a strong heartbeat, a sensations of interruptions in the work of the heart, anxiety, lack of air. Reduction of cardiac output in extrasystole leads to a decrease in coronary and cerebral blood flow and can lead to the development of angina pectoris and transient disorders of cerebral circulation (fainting, paresis, etc.). Extrasystoles increase the risk of [[atrial fibrillation]] and sudden death. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This pathology can be detected using ECG Dongle [https://cardio-cloud.ru/good/1], ECG Dongle Full [https://cardio-cloud.ru/good/2] and «Serdechko» [https://cardio-cloud.ru/good/12]. | ||
Latest revision as of 12:57, 31 March 2021
Extrasystole (premature contractions) is untimely depolarization and contraction of the heart or its individual chambers, it is the most frequently recorded form of arrhythmias. Extrasystoles can be found in 60-70% of people. Basically they are functional (neurogenic), their appearance is provoked by stress, smoking, alcohol, strong tea and especially coffee. Extrasystoles of organic origin arise from damage to the myocardium (ischaemic heart disease, cardiosclerosis, dystrophy, inflammation). [1]
It is manifested by the sensation of a strong heartbeat, a sensations of interruptions in the work of the heart, anxiety, lack of air. Reduction of cardiac output in extrasystole leads to a decrease in coronary and cerebral blood flow and can lead to the development of angina pectoris and transient disorders of cerebral circulation (fainting, paresis, etc.). Extrasystoles increase the risk of atrial fibrillation and sudden death.
This pathology can be detected using ECG Dongle [1], ECG Dongle Full [2] and «Serdechko» [3].