Difference between revisions of "Third-degree or complete atrioventricular block"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
* Hypertension and aortic and / or mitral stenosis, are believed to contribute to the degeneration of the conduction system, caused by fibrosis and calcification. | * Hypertension and aortic and / or mitral stenosis, are believed to contribute to the degeneration of the conduction system, caused by fibrosis and calcification. | ||
* Myotonic dystrophy forms 1 and 2 is neuromuscular diseases that are inherited in an autosomal dominant trait, in which heart affection is the disorder in formation of an impulse, and especially the disorder of AV conductivity. They begin as an asymptomatic increase in the duration of the P-R interval and can lead to complete atrioventricular block. It is possible fainting and sudden death, so patients need to install a permanent pacemaker. | * Myotonic dystrophy forms 1 and 2 is neuromuscular diseases that are inherited in an autosomal dominant trait, in which heart affection is the disorder in formation of an impulse, and especially the disorder of AV conductivity. They begin as an asymptomatic increase in the duration of the P-R interval and can lead to complete atrioventricular block. It is possible fainting and sudden death, so patients need to install a permanent pacemaker. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This pathology can be detected using ECG Dongle [https://cardio-cloud.ru/good/1] and ECG Dongle Full [https://cardio-cloud.ru/good/2]. | ||
Latest revision as of 12:39, 31 March 2021
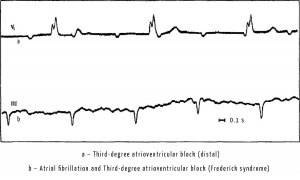
When third-degree or complete atrioventricular block occurs, atrial are stimulated by the main pacemaker (sinus node). Therefore there will be P wave on the ECG, recorded with a certain constant frequency (e.g., 90 beats per minute), and P-P intervals, measured at different sectors of ECG tape, will be the same. The ventricles are stimulated under the influence of impulses from the AV-connection (below the block) or from the bundle of His.
Clinical manifestations: Symptoms include weakness, dizziness, decreased exercise tolerance, syncope, reduced growth and development (in infants) and congestive heart failure. Patients with blocks, located under AV node, tend to show more severe symptoms, since the lower the site of the block is, the lower the frequency of the independent focus of excitation, located below, and lower reliability of its functioning.
Causes:
- Postoperative third-degree or complete atrioventricular block is the most common cause of acquired atrioventricular block in children caused by trauma to the atrioventricular node during cardiac surgery. In these patients, there is not only a very slow heart rate, but they also have a tendency to asystole with a high risk of sudden death.
- Complete atrioventricular block may caused by systemic infectionsб which are accompanied by inflammation of the myocardium and infiltration, such as diphtheria, Lyme disease (caused by Borrelia burgdorferi), Chagas disease, a fever of rocky mountains, iersineoz (Yersinia enterocolitica), infectious mononucleosis, bacterial endocarditis, viral myocarditis.
- Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that originated from the throat infection, caused by streptococcus group A, and expressed by systemic lesions. In the presents of acute rheumatic heart disease all of the layers of the heart may be included in the process of affection. While most patients have asymptomatic rheumatic heart disease, it is resulting in developing of damages of mitral and / or aortic valve, which can lead to regurgitation, and even congestive heart failure. As for rhythm disturbances in patients with rheumatic heart disease, they may experience tachycardia, which is disproportionate to manifestations of fever, and varying degrees of heart block. The most common type of atrioventricular block is the first-degree atrioventricular block.
- Reiter's Syndrome is seronegative arthropathy, which may be accompanied by pancarditis and varying degrees of atrioventricular block.
- Ischemia (e.g., Kawasaki disease, systemic arteritis) or infarction of left ventricular myocardial bottom wall may lead to transient or permanent disturbance of conduction, resulting in varying degrees of atrioventricular block.
- Hypertension and aortic and / or mitral stenosis, are believed to contribute to the degeneration of the conduction system, caused by fibrosis and calcification.
- Myotonic dystrophy forms 1 and 2 is neuromuscular diseases that are inherited in an autosomal dominant trait, in which heart affection is the disorder in formation of an impulse, and especially the disorder of AV conductivity. They begin as an asymptomatic increase in the duration of the P-R interval and can lead to complete atrioventricular block. It is possible fainting and sudden death, so patients need to install a permanent pacemaker.
This pathology can be detected using ECG Dongle [1] and ECG Dongle Full [2].