Difference between revisions of "Sinus tachycardia"
From CardioWiki
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[en:Sinus tachycardia]] | [[en:Sinus tachycardia]] | ||
[[ru:Синусовая тахикардия]] | [[ru:Синусовая тахикардия]] | ||
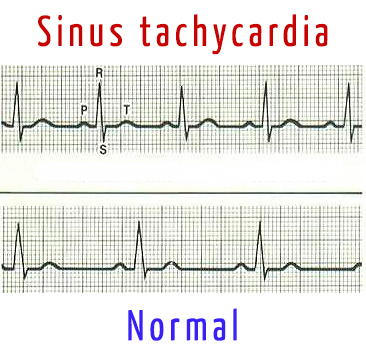
| − | [[ | + | [[File:Sinus_tachycardia.jpg|right]]<b>Sinus tachycardia</b> is a form of supraventricular tachyarrhythmia, characterized by an accelerated [[sinus cardiac pacemaker|sinus rhythm]] (i.e., the rhythm of the sinus node) with a heart rate of more than 90 beats per minute in adults. |
Clinical value has a sinus tachycardia, which remains at rest. Often it is accompanied by unpleasant sensations of "palpitation", a feeling of lack of air, although some patients may not notice an increase in heart rate. The causes of such a tachycardia can be both extracardiac factors, and actually heart disease. | Clinical value has a sinus tachycardia, which remains at rest. Often it is accompanied by unpleasant sensations of "palpitation", a feeling of lack of air, although some patients may not notice an increase in heart rate. The causes of such a tachycardia can be both extracardiac factors, and actually heart disease. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
# positive P wave in leads I, II, aVF, V4-V6; | # positive P wave in leads I, II, aVF, V4-V6; | ||
# with a pronounced sinus tachycardia, the PQ (R) interval is shortened (but not less than 0.12 s) and the duration of the QT interval is decreased, the amplitude of P wave in the leads I, II, aVF is increased, the amplitude of the T wave is increased or decreased, the upslopping ST segment depression(not more than 1.0 mm below the isoline). | # with a pronounced sinus tachycardia, the PQ (R) interval is shortened (but not less than 0.12 s) and the duration of the QT interval is decreased, the amplitude of P wave in the leads I, II, aVF is increased, the amplitude of the T wave is increased or decreased, the upslopping ST segment depression(not more than 1.0 mm below the isoline). | ||
| + | |||
| + | This pathology can be detected using ECG Dongle [https://cardio-cloud.ru/good/1], ECG Dongle Full [https://cardio-cloud.ru/good/2] and «Serdechko» [https://cardio-cloud.ru/good/12]. | ||
Latest revision as of 11:40, 31 March 2021
Sinus tachycardia is a form of supraventricular tachyarrhythmia, characterized by an accelerated sinus rhythm (i.e., the rhythm of the sinus node) with a heart rate of more than 90 beats per minute in adults.
Clinical value has a sinus tachycardia, which remains at rest. Often it is accompanied by unpleasant sensations of "palpitation", a feeling of lack of air, although some patients may not notice an increase in heart rate. The causes of such a tachycardia can be both extracardiac factors, and actually heart disease.
Sinus tachycardia is characterized by:
- increase in heart rate more than 90 beats per minute;
- maintaining the right sinus rhythm;
- positive P wave in leads I, II, aVF, V4-V6;
- with a pronounced sinus tachycardia, the PQ (R) interval is shortened (but not less than 0.12 s) and the duration of the QT interval is decreased, the amplitude of P wave in the leads I, II, aVF is increased, the amplitude of the T wave is increased or decreased, the upslopping ST segment depression(not more than 1.0 mm below the isoline).
This pathology can be detected using ECG Dongle [1], ECG Dongle Full [2] and «Serdechko» [3].